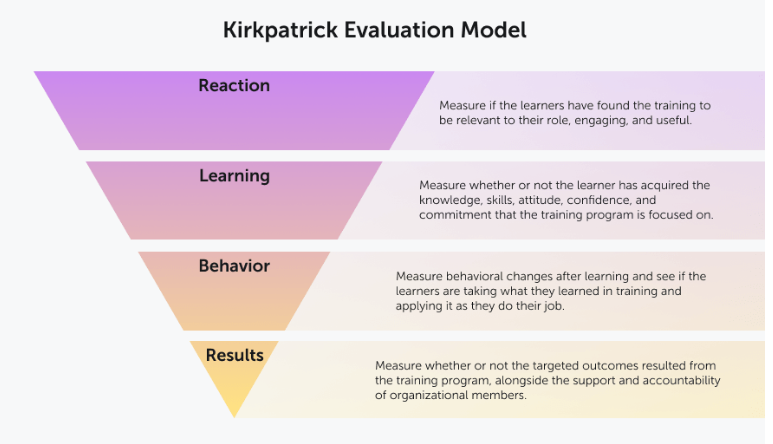
Kirkpatrick evaluation model
Level 1: Reaction
The first level of criteria is “reaction,” which measures whether learners find the training engaging, favorable, and relevant to their jobs. This level is most commonly assessed by an after-training survey (often referred to as a “smile sheet”) that asks students to rate their experience.
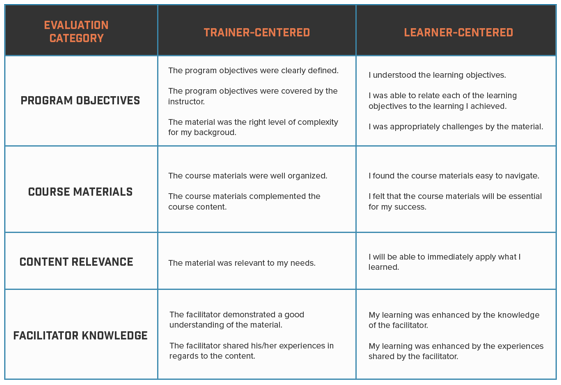
Focus can be on either the learners or the trainers:
Examples of resources and techniques for level one:
- Online assessment that can be graded by delegates/evaluators.
- Interviews
- Can be done immediately after the training ends.
- Are the participants happy with the instructor(s)?
- Did the training meet the participant’s needs?
- Are the attendee’s happy with the educational tools employed (e.g., PowerPoint, handouts etc)
- Printed or oral reports provided by delegates/evaluators to supervisors at the participants’ organizations.
- “Smile sheets”.
- Comment forms determined by subjective individual reaction to the training course.
- Post-training program questionnaires.
- Verbal responses that can be taken into consideration and considered.
- Especially encourage written comments
- Try to get honest responses and feedbacks
Level 2: Learning
The focus here is on the learning of each participant based on whether learners acquire the intended knowledge, skills, attitude, confidence and commitment to the training. Learning can be evaluated through both formal and informal methods, and should be evaluated through pre-learning and post-learning assessments to identify accuracy and comprehension. Methods of assessment include exams or interview-style evaluations.
Examples of tools and procedures for level two:
- Measurement and evaluation is simple and straightforward for any group size.
- You may use a control group to compare.
- Exams, interviews or assessments prior to and immediately after the training.
- Observations by peers and instructors
- Strategies for assessment should be relevant to the goals of the training program.
- A distinct clear scoring process needs to be determined in order to reduce the possibility of inconsistent evaluation reports.
- Interview, printed, or electronic type examinations can be carried out.
- An interview can be carried out before and after the assessment, though this is time-consuming and unreliable.
Level 3: Transfer /Behaviour
This level analyzes the differences in the participant’s behavior at work after completing the program. Assessing the change makes it possible to figure out if the knowledge, mindset, or skills the program taught are being used the workplace. This level starts 3–6 months after training.
Examples of assessment resources and techniques for level three:
- This can be carried out through observations and interviews.
- Evaluations have to be subtle until change is noticeable, after which a more thorough examination tool can be used.
- Were the learned knowledge and gained skills used?
- Surveys and close observation after some time are necessary to evaluate significant change, importance of change, and how long this change will last.
- Online evaluations tend to be more challenging to integrate. Examinations are usually more successful when incorporated within present management and training methods at the participant’s workplace.
- Quick examinations done immediately following the program are not going to be reliable since individuals change in various ways at different times.
- 360-degree feedback is a tool that many businesses use, but is not necessary before starting the training program. It is much better utilized after training since participants will be able to figure out on their own what they need to do different. After changes have been observed over time then the individual’s performance can be reviewed by others for proper assessment.
Level 4: Results
Commonly regarded as the primary goal of the program, level four determines the overall success of the training model by measuring factors such as more efficient and productive work execution.
Types of assessment strategies and tools used for level four:
- It should be discussed with the participant exactly what is going to be measured throughout and after the training program so that they know what to expect and to fully grasp what is being assessed.
- Use a control group
- Allow enough time to measure / evaluate
- No final results can be found unless a positive change takes place.
- Improper observations and the inability to make a connection with training input type will make it harder to see how the training program has made a difference in the workplace.
Sources:
https://www.valamis.com/hub/kirkpatrick-model
https://www.ardentlearning.com/blog/what-is-the-kirkpatrick-model
https://educationaltechnology.net/kirkpatrick-model-four-levels-learning-evaluation/

